Google Lashes Out at Android Dev
By Katherine Noyes
LinuxInsider
Part of the ECT News Network
09/29/09 4:00 AM PT
Google is under fire in the Android community, where some developers have not taken kindly to its heavy-handed "cease and desist" action against CyanogenMod. The fuming is not so much over whether Google is on solid legal ground -- that much seems clear -- but rather over its failure to take a more collaborative approach to solving the problem.
Google (Nasdaq: GOOG)  sent shock waves through the Android community late last week by launching a cease-and-desist order at well-regarded modder Cyanogen for bundling some of its closed-source applications with his CyanogenMod ROM.
sent shock waves through the Android community late last week by launching a cease-and-desist order at well-regarded modder Cyanogen for bundling some of its closed-source applications with his CyanogenMod ROM.
CyanogenMod is a free, heavily optimized build of Android 1.5r2 that focuses on performance and reliability. Its developer -- Steve Kondik, also known as "Cyanogen" -- claims some 30,000 users for the firmware product, which bundles closed-source Google apps such as Gmail, Market, Talk and YouTube  .
.
"Google just cease and desisted me," wrote Kondik in a short chat transcript uncovered by Android and Me last Thursday. "Cyanogenmod is probably going to be dead. I'm opening a dialogue with them."
Kondik did not respond in time to LinuxInsider's requests for comment on Monday. The official CyanogenMod site, meanwhile, has been unavailable due to the controversy's "Slashdot effect," Kondik wrote in a Twitter  post.
post.
'Nurturing' the Platform
CyanogenMod enhances the Android platform with extra functionality including multitouch capabilities and an improved user experience -- such as by providing five home screens instead of the usual three, according to reports.
Kondik's product has also reportedly spurred innovation in the development community.
"Countless other developers have sourced his work to breathe new innovation into their own creations and making it more stable or functional or both," wrote Mobility Site blogger Tariq Bamadhaj, for example. "In short, if Google gave birth to Android, Cyanogen was the one who nurtured and continues to nurture this growing baby."
'These Apps Aren't Open Source'
Google, for its part, attempted to respond and clarify its position through a post from Android developer Dan Morrill on Friday.
"I've noticed some confusion around what is and isn't part of Android's open source code," Morrill wrote.
Android apps for Google services like YouTube, Gmail and Google Voice "are Google's way of benefiting from Android in the same way that any other developer can, but the apps are not part of the Android platform itself," Morrill explained.
"These apps aren't open source, and that's why they aren't included in the Android source code repository," he asserted. "Unauthorized distribution of this software  harms us just like it would any other business, even if it's done with the best of intentions."
harms us just like it would any other business, even if it's done with the best of intentions."
Google spokesperson Carolyn Penner declined to provide additional comment.
"We don't have much more to say beyond what was included in the blog post," she told LinuxInsider.
'I Intend to Respect That'
On Monday, Kondik posted an update on the situation on the CyanogenMod site, which was viewable in Google's cache.
"What has become clear now is that the Android Open Source Project is a framework," Kondik wrote. "It's licensed in such a way so that anyone can take it, modify it to their needs, and redistribute it as they please. Android belongs to everyone. This also means that big companies [like] Google, HTC, Motorola (NYSE: MOT)  , and whomever else can add their own pieces to it and share these pieces under whatever license they choose.
, and whomever else can add their own pieces to it and share these pieces under whatever license they choose.
"The issue that's raised is the redistribution of Google's proprietary applications like Maps, GTalk, Market, and YouTube," he added. "These are not part of the open source project and are only part of 'Google Experience' devices. They are Google's intellectual property and I intend to respect that."
'A Bare Bones ROM'
Kondik will no longer distribute the apps as part of CyanogenMod.
Rather, "what I intend to do is simply ship the next version of CyanogenMod as a 'bare bones' ROM," he wrote. "You'll be able to make calls, MMS, take photos, etc. In order to get our beloved Google sync and applications back, you'll need to make a backup first. I'm working on an application that will do this for you."
Nevertheless, many in the open source community are now questioning Google's commitment to its open source offspring.
Not So Open?
"Google throws the 'open' out of 'open-source' by shutting down Android mod" read one headline, for example. Scores of comments on sites across the blogosphere expressed similar sentiments.
Several petitions are circulating -- on PetitionSpot and on Cyrket, for example -- urging fans to help save CyanogenMod.
An Android developer who reportedly works for Google's Morrill, meanwhile, wrote in a tweet on Friday, "To my Apple (Nasdaq: AAPL)  , Microsoft (Nasdaq: MSFT)
, Microsoft (Nasdaq: MSFT)  and Palm (Nasdaq: PALM)
and Palm (Nasdaq: PALM)  buddies: are you hiring to work on mobile stuff?"
buddies: are you hiring to work on mobile stuff?"
'A Confrontational Approach'
It is surprising that Google "took a more confrontational approach rather than contacting the developer directly in order to sort out the differences," Stephen Schultze, associate director of the Center for Information Technology Policy at Princeton University, told LinuxInsider.
Google's intellectual property claims are "legitimate and understandable," but there is probably "a reasonable 'third way' solution," Schultze added.
To wit: Cyanogen's own proposed solution, "divorcing his code base from the proprietary elements," may mean the developers are "on their way to solving the legal issues by creating a simple way for end-users to patch in their legal copies of the proprietary Google apps," he noted. "I would hope that Google would consider ways in which it could facilitate this process from its end."
Terms and Conditions
Android "has spawned a plethora of individuals and companies leveraging that platform with their own products," Raymond Van Dyke, a technology attorney in Washington, told LinuxInsider. "Since Google has expended considerable sums to roll out their paradigm, they naturally wish to maintain some control over it," he added.
Cyanogen's CyanogenMod "got Google's attention" by rolling various modules of Android into a bundled and popular product, Van Dyke noted -- "hence the cease and desist letter to let them know that this behavior  was not OK."
was not OK."
Indeed, in Android's Terms and Conditions, Google not only expressly says that it retains all intellectual property, but it "also states that 'you agree that Google may stop (permanently or temporarily) providing the Android Software Development Kit (SDK) (or any features within the SDK) to you or to users generally at Google's sole discretion, without prior notice to you," Van Dyke pointed out.
'Not Just Google'
Cyanogen's attempts to work around the problem will likely be permitted "so long as they avoid Google's IP," Van Dyke concluded. "Good luck!"
Looking ahead, in fact, luck may be just what Cyanogen needs.
"We are also trying to deal with the issue of htc/ti/qualcomm proprietary stuff," Kondik wrote in a tweet on Monday afternoon. "It's not just google.
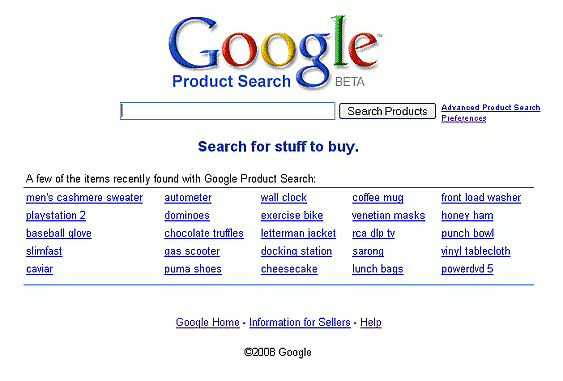
![Screen shot of Google Product Search results for [ watches children ]](http://www.googleguide.com/images/googlePrdSrchChildrensWatches1.gif)
![Google Product Search results for [ watches children ] using grid view](http://www.googleguide.com/images/googlePrdSrchChildrensWatches2.gif)
![Google Product Search results for [ watches children timex ]](http://www.googleguide.com/images/googlePrdSrchChildrensWatches3.gif)
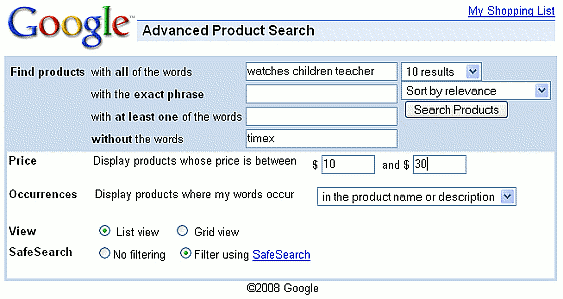
![Google Product Search results for [ watches children teacher ]](http://www.googleguide.com/images/googlePrdSrchChildrensWatches4.gif)



 During Where 2.0 yesterday, the company which is behind the technology of
During Where 2.0 yesterday, the company which is behind the technology of  Krishna further says "Our relationship with newspapers is symbiotic; we sent traffic directly to the content provider and we do not have special relationships, and we amplify the amount of news being read." "I am hoping, he says," to have all newspapers participate with Google News; for our readers we want an interesting debate that makes them think."
Krishna further says "Our relationship with newspapers is symbiotic; we sent traffic directly to the content provider and we do not have special relationships, and we amplify the amount of news being read." "I am hoping, he says," to have all newspapers participate with Google News; for our readers we want an interesting debate that makes them think."
 When a search query is submitted to Google, it is routed to a data coop where monitors flash result pages at blazing speeds. When a relevant result is observed by one of the pigeons in the cluster, it strikes a rubber-coated steel bar with its beak, which assigns the page a PigeonRank value of one. For each peck, the PigeonRank increases. Those pages receiving the most pecks, are returned at the top of the user's results page with the other results displayed in pecking order.
When a search query is submitted to Google, it is routed to a data coop where monitors flash result pages at blazing speeds. When a relevant result is observed by one of the pigeons in the cluster, it strikes a rubber-coated steel bar with its beak, which assigns the page a PigeonRank value of one. For each peck, the PigeonRank increases. Those pages receiving the most pecks, are returned at the top of the user's results page with the other results displayed in pecking order.



